Challenges in Rubber Industry
By Dr. Samir Majumdar
Flat : H-701, Neel Padm Kunj, Vaishali,
Opp. Dabur Chawk, Ghaziabad. India.
Introduction
Today’s hot topic is energy, particularly in
the scenario when crude price is increasing almost everyday. Energy is
definitely an essential element of today’s society. We can not even dream
without energy. People simply expect it – and demand it and therefore, people
of today virtually takes it for granted that it is there, you pay for and have
it. Number of times every day – at the touch of a switch, turn of a key or push
of a small button – energy is delivered instantly.
Today’s energy is used in cultivation, creating products,
product movement, generating commerce in safer, stronger, and more efficient
than at any time in the history. With on going liberalization process there has
been a drastic change in the Indian economy and there is a sign of positive
growth of both Agricultural and Industrial production. Automobile industry
growth in any country is driven from growth on the transportation. India’s
transportation growth is basically driven from agricultural growth.
Historic trend of agricultural growth in India
is 7 – 8% whereas, for Automobile industry, it is 5 – 6% and the exceptional
year was 2003 and 2004 where the Automobile industry has shown growth close to
14%
In the year 2004, the average growth of vital
truck segment has been recorded to above 12%. Average passenger car growth has
been close to 10%. Scooter growth rate has been 9% and motorcycle growth rate
by 7%. OTR growth rate has been close to 5% per annum. The above growth rate
figure is of OEM.
Some of the major OEM manufacturers in India
are Maruti, Toyota, Ford, Hyundai, General Motor, Honda City, Fiat, Telco,
Mercedes, Mitsubishi, Mahendra & Mahendra, Swaraj Mazda, Volvo, TVS, Bajaj Auto,
Hero Honda, Suzuki Motor etc.
Some of these foreign companies have taught us
good practices in quality processes lke 5S, TPM, TQM etc. for industry
discipline, managing product processing, defects, managing inventory and
dispatching to customer for highest level of customer satisfactions, customer
relations and so on.
Future Growth of Indian Automobile
Rubber industry growth in all countries is
linked with growth of Automobile industry. Future growth of Indian Automobile
Industry is evident because of following :
-
Economical growth of 7-8%
(7.6% in 2004 – 2005)
-
India is the fifth largest
economy in the world
-
India has 3rd
largest GDP in the entire continent of Asia
-
A huge population of above
1.1 billion
-
Average income of lower middle
class and middle class people are increasing due to economical growth on the
investment policy by Government of India.
-
Constraints of Indian Railways
to meet the growing demand for passenger and goods transport.
-
Road transport is the major
link for essential goods to the rural masses and transportation of farm
produce to the cities.
-
Development of golden
quadrilateral and North-South & East-West Corridors National Highways.
-
More and more capacity
utilization in Automobile industries.
-
Easy financing for new and old
vehicle purchase.
India as a Leading Country in the World
Time has changed and is changing very fast.
Developed nations are looking at India with more respect now. Indian
contribution in the ancient ages had been known but unfortunately these were not
been well communicated to the rest of the world and many of these information
were lost under the shadow of British rule in India over a period of 200 years.
Many important information are coming now, were not known to the world.
Presently India is world’s largest democracy
and world’s 4th largest economy. 15 of the world’s major Automobile
makers are obtaining components from Indian companies. This business fetched
India $1.5 billion in 2003, and will reach $15 billion by 2007. World-renowned
TQM expert Yasutoshi Washio predicts that Indian manufacturing quality will over
take that of Japan in 2013. Some more highlights in a nutshell are :
-
India is more than 5000 year
old ancient civilization.
-
India first invented the
Number System. Zero was invented by Aryabhatta. The place value system, the
decimal system was developed in India in 100 BC.
-
Aryabhatta was the first to
explain spherical shape, size, diameter, rotation and correct speed of Earth
in 499 AD.
-
The World’s first university
was established in India in Takshila in 700 BC. Students from all over the
World studies more than 60 subjects.
-
The University of Nalanda
built in the 4th century was one of the greatest achievements of
ancient India in the field of education.
-
Sanskrit is considered the
mother of all higher languages. Sanskrit language is known to be the most
precise, and therefore suitable language for computer software-a report in
Forbes magazine, July 1987.
-
There are 325 languages spoken
in India, have 1652 dialects and having 18 official languages, which is very
unique anywhere in the World within 29 states, and 5 union territories.
-
Having population close to
1.3bn within an area of 7516 KM – coastline.
-
There are 5600 dailies, 15000
weeklies and 20000 periodicals in 21 languages with combined circulation of
142 million.
-
Current GDP rate close to 8%,
$576bn.
-
India is the largest English
speaking Nation in the world and 2nd largest pool of Engineers and
Scientist in the World.
-
McKinsey believes India’s
revenue from the IT industry will reach $87 bn by 2008.
-
Flextronics, the $14 bn global
major in Electronic manufacturing services, has announced that it will make
India a global competence centre for telecom software development.
-
Tata Motors paid $118 mn to
buy Daewod commercial vehicle company of Korea.
-
Ranbaxy, the largest Indian
pharmaceutical company, gets 70% of its $1 bn revenue from overseas operations
and 40% from USA.
-
India is one of the world’s
largest diamond cutting and polishing centres, its exports were worth $6bn in
1999. About 9 out of 10 diamond stones sold anywhere in the world, pass
through India.
-
Mobile phones are growing by
about 1.5 mn a month. Long distance rates are down by two-thirds in five
years and by 80% for data transmission.
-
Wal-Mart sources $1 bn worth
of goods from India – half its apparel. Wal-Mart expects this to increase to
$10 bn in the next couple of years.
-
India’s INSAT is among the
world’s largest domestic satellite communication systems.
-
India’s Geo-synchronous
Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) was indigenously manufactured with most of the
components like motor cases, inter-stages, heat shield, cryogenic engine,
electronic modules all manufactured by public and private Indian industry.
-
India is providing aid to 11
countries, writing-off their debt and loaning the IMF $300M. It has also
prepaid $3bn owed to the World Bank and Asian Development Bank.
-
The Indian pharmaceutical
industry at $6.5bn and growing at 8-10% annually, is the 4th
largest pharmaceutical industry in the world, and is expected to be worth $12
bn by 2008.
-
Its exports are over $2 bn.
India is among the top five bulk drug makers and at home, the local industry
has edged out the Multi_national companies whose share of 75% in the market is
down to 35%. Trade of medicinal plants has crossed $900M already.
-
There are 170 biotechnology
companies in India, involved in the development and manufacture of genomic
drugs, whose business is growing exponentially.
-
With more than 250
universities, 1,500 research institutions and 10,428 higher-education
institutes, India produces 200,000 engineering graduates and another 300,000
technically trained graduates every year. Besides, another 2 million other
graduates quality out in India annually.
-
The Indian Institute of
Technology (IIT) is among the top three universities from which McKinsey &
Company, the world’s biggest consulting firm, hires most.
Rubber Products
India can produce now all types of rubber
products beginning from critical applications in information technology,
footwear, cables, pharmacy, critical products of passenger car profiles, hose,
conveyor belt, transmission belts, V-belts, gasket, oil seals to higher rated
passenger car tyre and all steel truck tyres for domestic use as well as for
exporting to abroad.
As on today, India is making more than 35000
different kinds of rubber products in 6000 different units all over India for
domestic as well as for export whose turn over is close to US$ 5 bn per annum.
Out of these 6000 units, roughly estimates are :
-
30 number of large scale units
-
300 number of medium scale
units and
-
5600 number of small scale
units
Today large and medium sectors are not so much
in threat as much as small sectors. Large and medium sectors have money power
and they have options for diversification, which may not be true for small
sectors and their current situation, is either survive or die. Today’s major
challenge for small sectors are on cost, quality and productivity.
Challenges
Our present challenges are with the small-scale
units and the major challenges are how they can cope up in the current scenario
of :
-
Global Competition
-
Rising Fuel Cost
-
Rising Raw Material Cost
-
Reduction in Import Duty
Our Potentials
Our scope and potentials are plenty. When
Japan’s rubber kg per person is close to 14, India is having only less than 1 kg
(Fig. 1) Other advantages of India in rubber fields are :
-
Large producer of NR (Consumed
approximately 1.0m MT of rubber in 2005)
-
India is 4th
largest consumer of Rubber
-
Large domestic market
-
Rapid growth of automobile
sector
-
Academic based technologists
-
On going economical reforms
Rubber Consumption Pattern

Fig. 1. Rubber Consumption Pattern.
1-India, 2-China, 3-Europe, 4-North America, 5-Japan.
New Concept
What we really need now is better understanding
in the business. It is not enough that we know making a product and the
existing profit margin in the domestic market is also known. Our strategy needs
to be changed entirely from domestic market focus to international market
focus.
India’s small scale industry is driven by
business community. In most cases the owner becomes the technical man,
marketing man, quality man, production man, commercial man etc. – which means
the owner is everything. In most cases owner’s relatives will be holding all
key position in the organization and as a result multifunctional communication
is lost and finally loses the opportunity for the future growth of the company.
We need to bring the concept of R&D center very
fast in small manufacturing sectors. R&D center does not mean purchasing of
costly equipments and publishing of theoretical papers in different journals.
R&D center in small organization should work in harmony with production,
marketing and customer.
At least all manufacturing organization,
however small it is, will have a quality control department for controlling
incoming raw material, process and identifying the quality of product suitable
for customers. R&D center can be made as a special wing from existing Quality
Control department only.
R&D center performs the company objectives
today, tomorrow and after 5-10 years from now. Which means R&D center
practically provides business directives for present and future. This is very
true in all developed nations. We need to bring on these concepts as fast as
possible.
R&D Center (Provides Business Directives)
Indian R&D centers should take the advantages
of academic based technologists and train them as per company requirements. For
rubber industry alone India has 10 Degree Colleges, 2, Diploma Courses, 3 Post
Doctorate Research Institutes, 4 Research Institutes, 14 Testing Laboratories
and 6 Certifying Institutes. Selection of right candidate and training of them
are important in any organization and the next important part is to provide
atmosphere to retain those R&D executives.
A right R&D executive should have following :
-
Capability
-
Conceptual understanding
-
Confidence
-
Attitude
-
Dedication
-
Information exploration
attitude (Domestic/International)
-
Multilevel contacts
-
Educating internal customers
-
Continuous Resource
development
Most important part is an approach should be
made to monitor continuous resource finding in R&D center. They should be given
appropriate training and these executives, intern, can train others. Per need
of the company, an aim should be there for restructuring the R&D wing as and
when required.
As already emphasized, R&D concept can begin
from the existing quality control wing itself. For developmental jobs if
required out side testing may be considered, if the cost of the equipments are
not affordable. A time may come when out side testing will gradually become
expensive, only at that time it might be worth while to procure the equipment
for future cost reduction.
All Indian R&D Center has to be interactive
with Production and Marketing to give Business Directives (Fig.2). The most
important part, which is also lagging in our existing R&D center that any R&D
center has to be based on customer focus to integrate on raw material
requirement, processing requirement and quality of product suitable for
customers and finally gives business directives in the scenario of political
changes and economical changes.
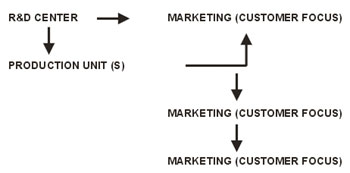
Fig.2 : R&D Center to be interactive with
Production and Making to give Business Directives.
Quality
All manufacturing industry will have a quality
wing for controlling in coming material, controlling process and the finished
goods. Quality of product is – Attributes Accepted by Customers.
Attributes could be anything, look, design,
performance, durability, comparison etc.
-
Design, Look
-
Performance
-
Durability
For acceptable level of quality, you need
appropriate technology. You may not compete any more with the old technology
you have. Modernisation of the manufacturing unit is a must and R&D can play
major role in that. Cost of quality are of two categories:
-
Cost of Lack of Quality
-
Cost of Achieving Quality
Cost of lack of quality can again be due to two
primary reasons; internal failure cost and external failure cost. External
failure costs are damaging since most cases this will be returned material from
the customers due to customer dissatisfaction and therefore it adds
transportation cost as well as the cost of losing the customers.

Fig.3 : R&D can Concentrate on Continuous Improvement of Product
When quality of the product is being
maintained, there are two types of costs; prevention cost and cost for
improvement and in the later part R&D can play the major role.
There has to be some technology background
through which the current product is being made. For improved quality in the
competitive scenario, better technology might be required and R&D can help in
Product Design and Development, Process Design and Development, Compounding
Design and Development, Finding alternatives, Development of man power etc.
R&D will be basically for all necessary
alternatives in the competitive market and it is to be focused on cost saving on
all activities in manufacturing the products. Practically R&D wing helps in
cost saving in developing the right product and right man power such that the
continuity of the right product is maintained. Concept of right product,
changes with time because the demand pattern in the society is changing
continuously.

Fig. 4 : Practically R&D
wing helps in cost saving in developing the right product and right man power.
-
Product Design and Development
-
Process Design and Development
-
Compounding Design and
Development
-
Finding alternatives
-
Development of man power
Reference
-
Manufacturing Profiles for
Automobiles. Dr. S. Majumdar, Rubber Chem Review (17-23) March-April 2005.
-
Carbon Black, Dr. Samir
Majumdar, Marketing In a New Era : A Global Perspective, Proceeding of Amity
Business School, Noida, at Banquet Hall, Hotel Ashoka, Chankyapuri, New Delhi,
Dec. 21, 2004.
-
Challenges, Prospects and
Vision of the Indian Rubber Products Manufacturing Industry, Shir Raghupati
Singhania, VC & MD – JK Industries Ltd., International Rubber Journal (24-28),
June 2005.
-
CBFS, Dr. Samir Majumdar,
Rubber Chem Review, July – August (17-23) 2005.