Articles - Rubber Technical Papers
INTRODUCTION
One of the key technological areas in which new advances are impacting
the rubber industry, is that of new physical testing and analytical tools.
With technological development in electronic sensors, data acquisition
and data analysis systems, enhancements and ew developmentarebeing made
continuously in material testing and analytical equipment.
In this paper I have selected a total of ten (10) key examples of recent
development in physical testing and analytical instruments for our discussion.
Because of time constraints, I will highlight here only the significance
of these developments and their applications to rubber industry. Additionally,
Appendices A and B, are included here listing commonly used physical tests
and analytical instruments by polymer / rubber R&D Laboratories.
ADVANCES IN PHYSICAL PROPERTY TESTS
DYNAMIC STRESS RELAXOMETER (DSR)
Rubber industry continously looks for tests that can determine/predict
processing characteristics of rubber compounds in manufacturing plants.
A successful and practical test should entail measurement of nervy nature
of materials and how they recover/relax when applied stress is released,
be simple, have short test time, and provide quality control information.
The DSR, a Uniroyal Goodrich patented tester, is such an insrument for
testing the responise of an elastomeric material after the application
of applied stress. The sample is put into the conical mould cavity and
is squeezed to a fixed thickness (1/4”). It is heated to the desired
temperature during a fixed time after which a small twist is applied on
the rotor to impart a sudden strain on the sample. The standard twist
angle is 20, however, the magnitude of the twist can be varied. The entire
test takes only 70 seconds.
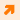
Peak torque (TM) is measured after the strain application, and the sample
relaxes. The area under the torque-time at two seconds is called torque
Summation (S 3). First time constant, t1, is the time at which torque
is reduced to 37% of TM. Second time constant, t2 is the time when torque
is reduced to 13% of TM Both, t1 and t1 are expressed in millieseconds.
See Figure 1. The DSR has on-board data acquistion and analysis system
and printer.
DSR OUTPUT
The DSR has proved to be very useful in many R&D and factory Processing
applications. Since it measures the elastic (nerve) and relaxation responses
of materials, it has shown excellent correlation between prediction and
actual processing behavior. Some examples are given here.
Two polybutadienes with idential Mooney values showed different processing
behavior in factory. The DSR measurements on raw polymers showed that
t2 and other long term relaxation times were different for those elastomers.
The DSR prediction agreed with factory processing.
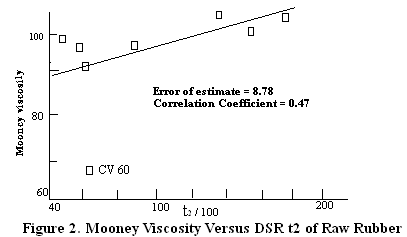
Figure 2. Mooney Viscosity Versus DSR t2 of Raw Rubber
Figure 2 shows several natural rubber samples showing ML-4 values fairly
close to each other, say between 90-100 range. One might conclude that
these would process alike. The DSR t2 data showed much greater differences
which agreed with the factory processing experience.
extent of variabillity of natural rubber polybutadienes for a six week
period at a tyre plant. For this reason, we now use DSR to classify incoming
natural rubber shipments into three categories; easy, moderatend difficult
(to process).
Observations of Variability of Natural Rubber and
PolybutadienceforSixweekPeriod at a Tire Plant.
relationship (1) between the Wallace Plasticity, Po and the DSR t2 values.
The DSR classification has considerably reduced any processing problem
due to NR variability.
data obtained over a three-month period on an NBR hose compound. Processi
ng difficulty was experienced after mid-February. The Ì2 DSR data
on raw rubber explained the change; Ì2 has increaseed from 8.5
to 10.8 N.m.s. indicating changes in relaxation properties. Money values,
however, did not show change. DSR was able to differentiate, and the Problem
was corrected.